이번에는 Embedding vector의 weight를 같게 하는 weight tying에 대해 연구한 Using the Output Embedding to Improve Language Models 논문에 대해 리뷰해보고자 한다. Transformer를 소개한 Attention is all you need 논문에서 인용되었고, Transformer의 embedding vector를 구성할 때 이 논문을 인용하며 same weight를 공유한다길래, 관심이 생겨서 읽어보게 되었다.
논문 원문 링크는 아래와 같다.
Using the Output Embedding to Improve Language Models
We study the topmost weight matrix of neural network language models. We show that this matrix constitutes a valid word embedding. When training language models, we recommend tying the input embedding and this output embedding. We analyze the resulting upd
arxiv.org
Introduction
우리가 흔히 접하는 Word Embedding matrix(여러 단어의 word embedding vector가 모여서 word embedding matrix가 된다.)
input word가 vector c=∈RC일때, 이 input word vector는 sparse representation을 가진다.
이를 dense representation으로 변환해주기 위해 word embedding을 사용한다. 자세한 내용은 아래의 링크를 참고 바란다.
워드 임베딩(Word Embedding)이란? (1)
워드 임베딩(Word Embedding) 자연어처리를 수행하는 시스템들은 입력을 텍스트로 받는다. (출력의 경우에는 다를 수 있다.) 그러나, 우리가 자연어처리를 하기 위해 사용하는 여러 모델들은 수치화
gbdai.tistory.com
다시 돌아와서, 이때 word embedding을 위해 사용하는 word embedding matrix를 U라고 해보자
word embedding은 U⊤c으로 수행되어진다. 이 word embedding 연산의 결과는 activation vector h2이다.
이 h2를 단어 당 score를 담고 있는 h3 vector(h3 vector는 추후 softmax가 적용됨으로써 단어 당 확률을 가진 vector가 된다.)로 투영해주는 second matrix V가 있다고 해보자.
second matrix V로 h3 vector로 투영해주는 연산은 h3=Vh2이다
이 때, U, V는 같은 size를 가지고 있다. 이를 알아보기 위해 LSTM 기반의 language model이라고 가정해보자.

다음과 같이 word vector c, word embedding matrix U, activation vector h2가 있다.
word vector는 one-hot encoding의 길이(즉, 단어의 개수) C의 크기를 가지고 있으며, word embedding matrix U는 C×H, h2는 LSTM의 hidden size H의 크기를 가지고 있다.

U⊤c 연산을 통해 word embedding이 수행됨을 확인할 수 있다.
이후 second matrix V가 h2를 단어 당 score를 담고 있는 h3 vector로 투영해주는 과정 Vh2은 아래와 같다.

여기서 , 우리는 U와 V가 C×H의 같은 size를 가지는 것을 알 수 있다.
논문에서는 U를 input embedding이라고 부르며, V를 output embedding이라고 부른다.
그러면서, input embedding과 output embedding matrix 모두 word embedding으로 사용되어질 수 있지만 input embedding만 사용되어지는 것을 지적하면서, 다음과 같은 연구를 진행하였다고 밝힌다.
- Input embedding과 output embedding의 quality 비교
- Output embedding을 이용한 neural network language model의 성능 향상
또한, 이러한 연구를 통해 아래와 같은 결과를 얻었다고 한다.
- Word2vec skip-gram model에서는 output embedding이 input embedding에 비해 살짝 열세한 성능을 보였다
- RNN 기반의 language model에서, output embedding은 input embedding보다 좋은 성능을 보였다
- 두 embedding matrix의 weight를 공유하는 "tying"을 한 joint embedding은 output embedding과 비슷하게 학습되었다.
- Input embedding과 output embedding을 "tying"함으로써 language model의 성능이 향상되었다.
- Dropout을 사용하지 않을 때, regularization을 적용할 수 있는 Projection Regularization(PR)을 제안한다.
- Weight tying은 model performance의 하락 없이 model의 size(number of parameters)를 줄일 수 있다.
Weight Tying
본 논문에서는 NNLMs(Neural network language models), word2vec skip-gram model, NMT model(neural machine translation) 각각에 weight tying을 적용해봤다고 한다. 또한, NMT model의 경우, three-way weight tying method(TWWT) 방법론을 제안한다.
연구에 사용된 NNLM model은 input embedding matrix, 2개의 LSTM layer(각각 h1과 h2), hidden scores/logits layer h3, softmax layer로 이루어져 있다. Loss function의 경우 규제가 없는 cross-entropy loss를 사용하였다.
논문에서는 Large model과 Small model, 2개의 NNLM model을 사용하였는데, large model의 경우 dropout을 사용하였고, small model은 dropout을 적용하지 않는다. 대신 regularization을 적용할 수 있는 새로운 방법론을 제안하는데, 바로 Projection Regularization(PR) 기법이다.
Projection Regularization(PR)기법은 간단하다. output embedding matrix 전에 projection matrix P∈RH×H를 넣어주고, small model의 loss function에 regularizing term λ‖P‖2를 넣어준다.
(이 때, λ=0.15로 설정했다고 한다.)
이를 통해, small model의 loss function은 gradient descent를 통해 학습하면서, loss뿐만 아니라 projection matrix P의 weight를 같이 줄여주면서 regularization을 적용하는 효과를 줄 수 있다.
이러한 Projection Regularization(PR)기법은, input embedding과 output embedding 위치에 same embedding을 사용할 수 있게끔 하면서 regularization도 적용시킬 수 있기 때문에 논문에서 제안하는 Weight Tying(WT)에 적합하다고 말한다.
이후, 논문에서는 untied NNLM과 tied NNLM을 비교하여 분석한다.
Untied NNLMs
Untied NNLMs, 즉 기존의 NNLM model이다.
Timestep t에서, 현재 input word sequence i1:t=[i1,…,it]와 current target output word ot일때, loss function인 negative loss likelihood function은 아래와 같다
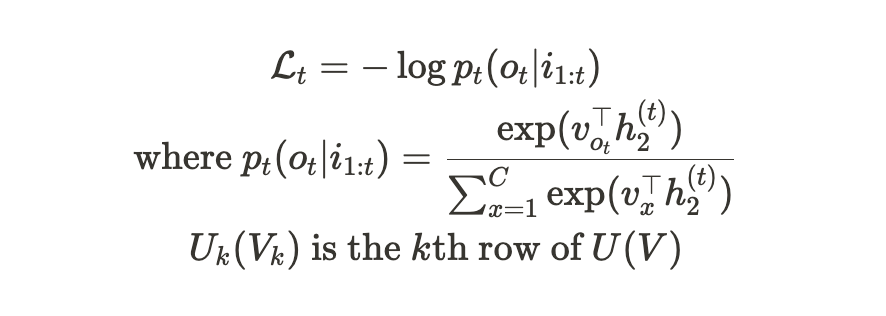
이 때, Uk(Vk)는 word k와 대응되는 U(V)의 row이며, (k라는 단어의 representation)
h(t)2는 timestep t일때, LSTM layer의 가장 위 layer의 output이다.
Optimization은 stochastic gradient descent를 사용하여 진행했다고 한다.
이러한 Untied NNLM model에서, input embedding의 row k의 update는 다음과 같다.
(논문에서는 단순함을 위해 timestep t일때, it≠ot라고 가정한다)
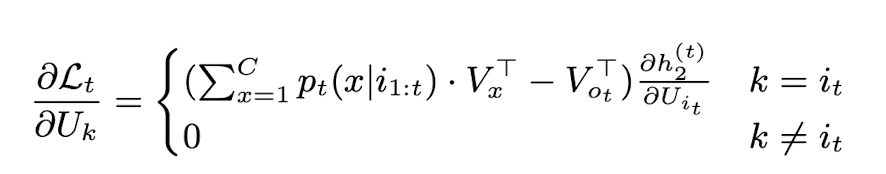
다음은 output embedding의 경우이다.
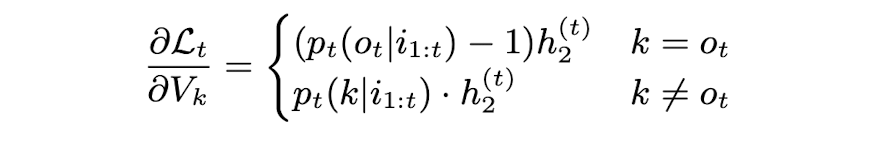
위 수식을 보면 알 수 있는 점은, 매 timestep마다, input embedding에서 update되는 row는 Uit만임을 알 수 있다.
즉 k=it일때만 update되고, k≠it일때는 gradient가 0이기에, update되지 않는다.
정리하자면, 현재 timestep에 대한 단어에 대한 embedding vector만 update되며, 이러한 현상은 input embedding matrix에서는 sequence에서 출현 빈도가 낮으면 update가 잘 안된다는 것을 의미한다.
output embedding의 경우, 이러한 문제 없이 매 timestep마다 잘 update됨을 확인할 수 있다.
Tied NNMLs
Tied NNML model에서는, input embedding과 output embedding이 tying(weight를 공유)하기 때문에, U=V=S라고 설정한다.
(여기서의 S는, input embedding과 output embedding 역할을 같이 하는 tied NNML model에서의 embedding matrix이다.)
S의 각 row의 update는 input과 output embedding 두 역할에서 얻어진 update를 더한 값이다.
즉, update 계산 mechanism은 위에서 살펴본 Untied NNLMs의 update와 같으나, embedding matrix S는 두 역할 모두 하니, input embedding 역할로 얻은 update와 output embedding으로써 얻은 update 모두 반영한다는 것이다.
k=it와 k≠it일때로 나눠서 살펴보자.
k≠it일때부터 살펴보자.
두 update를 더한 값이기 때문에 0+(pt(ot|i1:t)−1)⋅h(2)2, 혹은 0+pt(k|i1:t)⋅h(2)2이다.
(k≠it일때, k=ot일수도 있고 k≠ot일수도 있다.)
그런데, input embedding으로부터 오는 update가 0이기 때문에, 사실상 untied NNLMs의 output embedding과 유사하게 update된다고 볼 수 있다.
즉, k≠it 일때는 output embedding의 영향이 크다
k=it일때는 다르다.
이때에는 input embedding의 k=it일때의 update와, output embedding의 k≠ot일때의 update의 합으로 이루어진다.
(위에서 it≠ot라고 가정했기 때문에, k=it일 경우에 k=ot가 되면 가정과 맞지 않기 때문에 k≠ot일때의 경우밖에 없다.)
이 때, output embedding 부분의 update term은 pt(it|i1:t)⋅h(2)2가 되는데, pt(it|i1:t)의 경우, 단어가 연속적으로 두 번 출현할 확률은 0에 가깝기 때문에(timestep 1부터 t까지의 단어가 주어졌을때, timstep t의 단어가 나올 확률) 0에 가까울 것으로 예상된다.
(논문에서는 이러한 낮은 확률에 대해 실험적으로 증명되었다고 밝힌다.)
따라서 k=it일때는 input embedding의 영향이 더 크다.
각 iteration마다 S의 모든 row가 update되는데, k=it일때는 해당 row가 input embedding의 영향을 많이 받지만, 나머지 k≠it의 row들은 output embedding의 영향을 많이 받게 된다.
전반적으로, 각 iteration에서 각각의 row들은 k=it이어서 input embedding의 영향을 받는건 한 번씩이지만, k≠it인 나머지 timestep에는 모두 output embedding의 영향을 받기 때문에 tied embedding은 input embedding보다 output embedding과 더 높은 유사성을 보인다.
Weight Tying in Word2vec
Word2vec에서는, h(t)2가 identity function으로 바뀐 것 이외에는 NNLM과의 update rule에서의 변화는 없다.
다만 논문에서 Word2vec에서의 weight tying의 경우 pt(it|i1:t)가 0에 가까울 때, input과 output embedding의 decoupling을 유발하던 LSTM layer h(t)2가 identity function으로 바뀌었기 때문에, 적절하지 못하다고 말한다.
Weight Tying in Neural translation model
Neural translation model은 다음과 같이 정의된다.
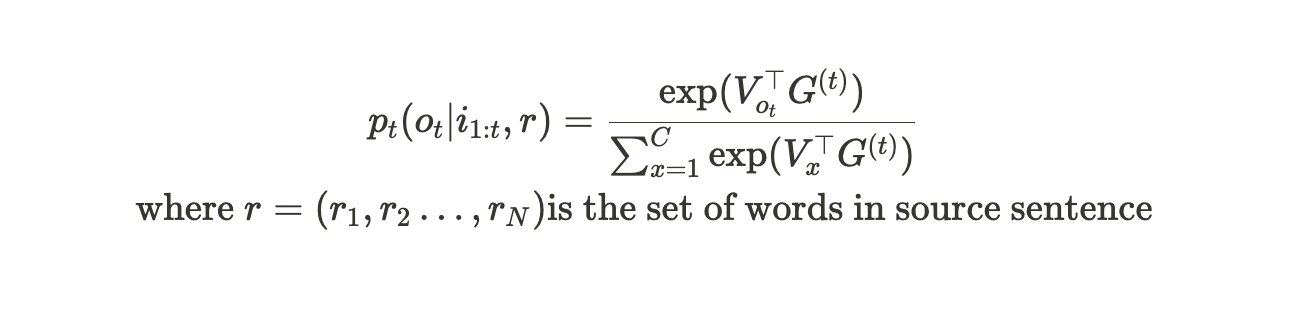
U,V는 각각 decoder의 input embedding, output embedding이며, W는 encoder의 input embedding이다.
G(t)는 decoder이며, context vector ct, input word로부터 오는 word embedding과 더불어 previous state를 입력으로 받는다. F는 encoder이다.
논문에서는, decoder의 input과 output embedding을 tie하여 weight tied translation model을 구성하였다고 한다.
그런데, 저자들은 한 가지 발견을 하게 된다. 바로 WMT 2014 EN->FR dataset과 WMT 2015 EN->DE dataset을 BPE 알고리즘을 이용하여 subword로 분절해본 결과, source language와 target language의 domain이 다름에도 불구하고 상당수의 subword를 공유한다는 것이다.

(그런데, 이러한 방법은 같은 독일어, 영어, 프랑스어는 비슷한 글자를 사용하기 때문에 가능한 것 같다. 한국어-영어와 같이 라틴 문자 계열이라는 공통점이 없는 source 와 target에 대한 한계가 있는 것 같다. 이 부분은 추후 다른 연구를 찾아봐야겠다.)
이러한 발견을 토대로, 저자들은 decoder의 input과 output embedding을 tie하는 것을 넘어, encoder의 input embedding까지 tie하는 Three way weight tying (TWWT)라는 것을 제안한다.
Results
그렇다면, 이와 같은 weight tying의 결과는 어떨까? 논문에서는 다양한 embedding의 quality에 대해 실험을 해보고, 그들의 유사성과 함께 tying의 효과를 연구했다고 한다.
Quality of Obtained Embeddings
저자들은 embedding의 quality에 대해서 실험해봤다고 한다.
Embedding된 word vector간의 cosine 유사도를 구하고, 사람이 판단한 strength of relationship과 비교하는 방법을 사용하였으며, 여기에는 Simlex999, Verb-143, MEN, Rare-Word, MTurk771이 사용되었다.
먼저, text8 dataset에서의 Word2vec model 결과이다.
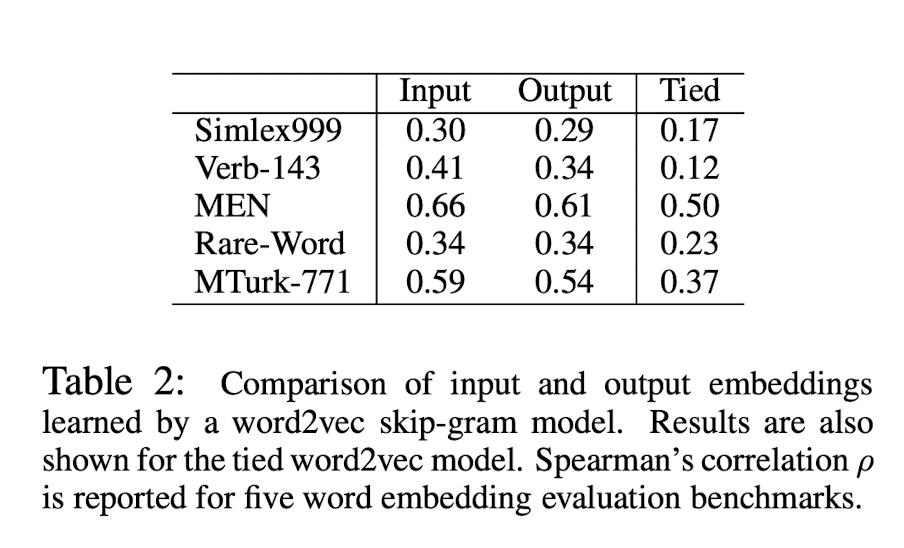
input embedding과 output embedding이 비슷한 성능을 냄을 확인할 수 있다.
다만, 위에서 잠깐 언급한 것처럼, word2vec에서의 weight tying은 word2vec에는 적절하지 못함을 확인할 수 있다.
다음으로는 small NNLM model을 PTB dataset과 text8 dataset으로 각각 training시킨 model의 결과이다.
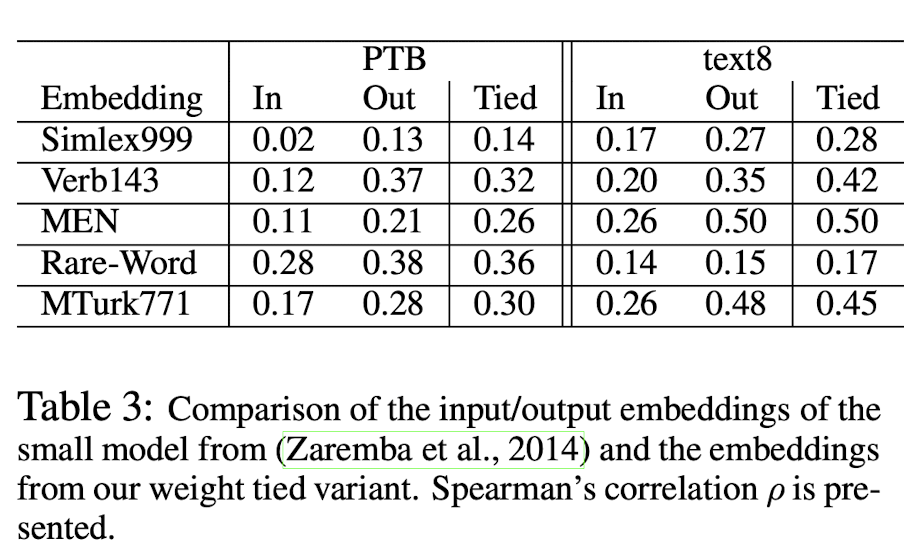
여기서는 input embedding이 output embedding보다 성능이 낮음을 확인할 수 있다. Tied embedding의 경우 output embedding과 비슷한 성능을 내는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
저자들은 아까 위에서 언급했던, tied embedding이 input embedding과 output embedding 중, 어떤 것의 영향을 더 받는지에 대해서도 실험해봤다. NNLMs에서 tied embedding의 경우, output embedding의 영향을 더 많이 받는다고 하였는데, 실제로 그러한지 결과를 봐보자.
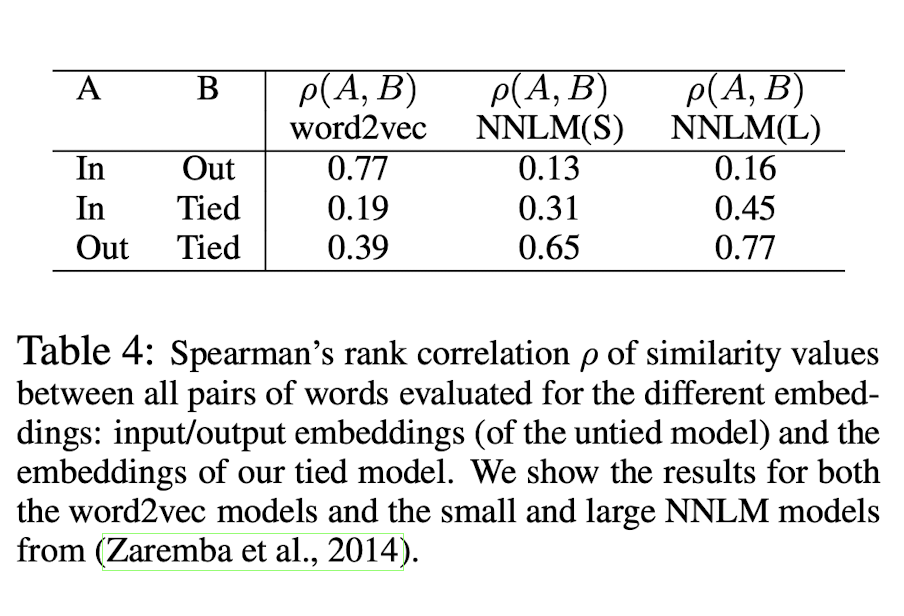
Word2vec의 경우, input embedding과 output embedding이 서로 비슷하고, tied와는 상당히 다른 것을 볼 수 있다.
그런데, NNLM의 경우, large model과 small model 모두 output embedding과 tied embedding이 유사하고, input embedding은 tied embedding과 다소 유사하지만 output embedding과는 다른 것을 확인할 수 있다.
위에서 언급한 NNLMs에서 tied embedding의 경우, output embedding의 영향을 더 많이 받는다는 것이 실험으로 증명된 것이다.
Neural Network Language Models
이번에는 embedding tying이 NNLM model의 성능에 어떠한 영향을 미쳤는지에 대한 실험 결과이다. model의 perplexity를 측정하는 방향으로 model 성능을 측정하였다.
Small model의 경우 encoder와 decoder의 LSTM layer가 각각 200 units을, large model의 경우 1500 units을 포함하였고, Large model은 3개의 dropout layer를 각각 LSTM layer 이전, h1과 h2 사이, h2 뒤에 배치하였다고 한다.
(dropout probability는 0.65로 설정하였다고 한다. 이외의 hyperparameter는 small large model이 같게 설정하였다.)
먼저, Large model을 PTB dataset으로 수행한 결과이다.
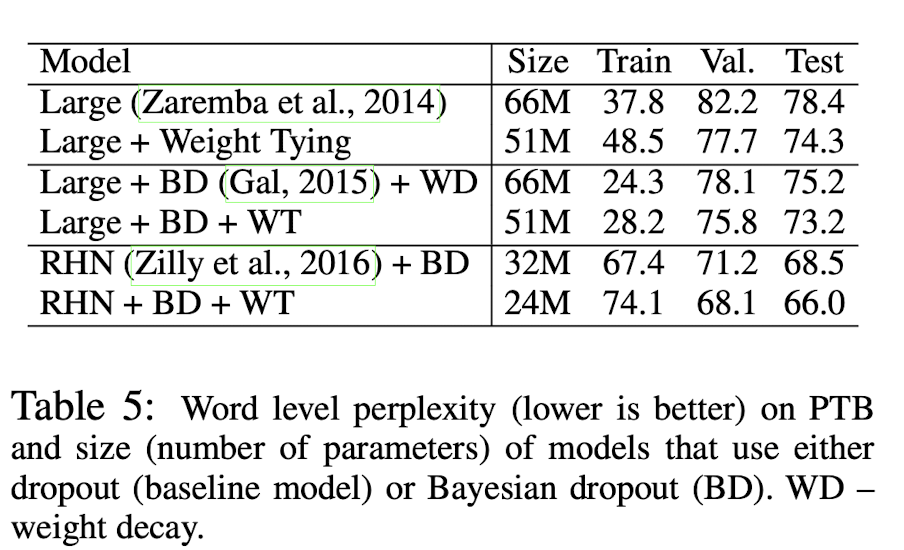
Weight tying(WT)이 적용된 model들은 valid, test perplexity가 감소했음을 확인할 수 있다.
다만, train perplexity는 증가하였는데, 논문에는 이 현상을 parameter 수가 감소하면서 overfitting이 덜 일어났기 때문에 나타난 현상이라고 말한다.
Small model의 결과는 아래와 같다. (small model에는 dropout을 적용하지 않는다.) PTB dataset에 대한 결과이다.
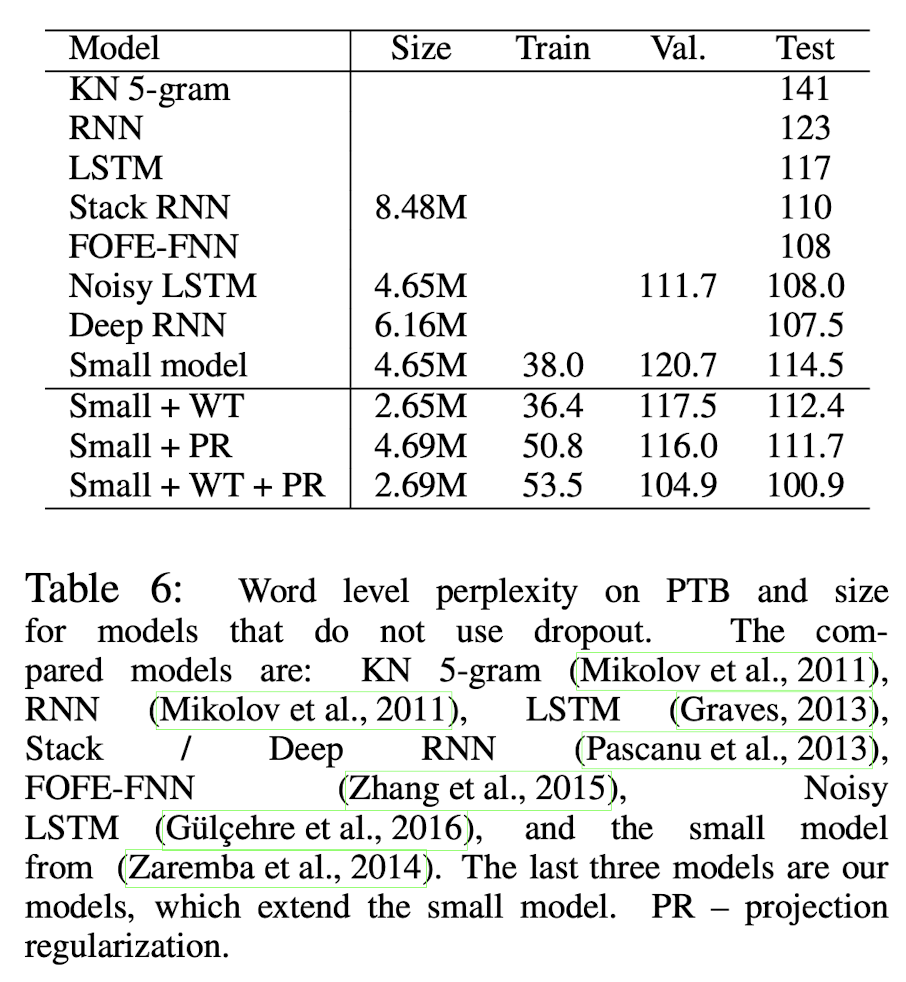
Weight tying(WT)기법과, 논문에서 제시한 Projection Regularization(PR)도 dropout 없이 유의미한 성능 향상을 이끌어냄을 확인할 수 있다.
논문에서는 두 기법을 combine 함으로써, 그 당시 SOTA를 달성하였다고 한다.
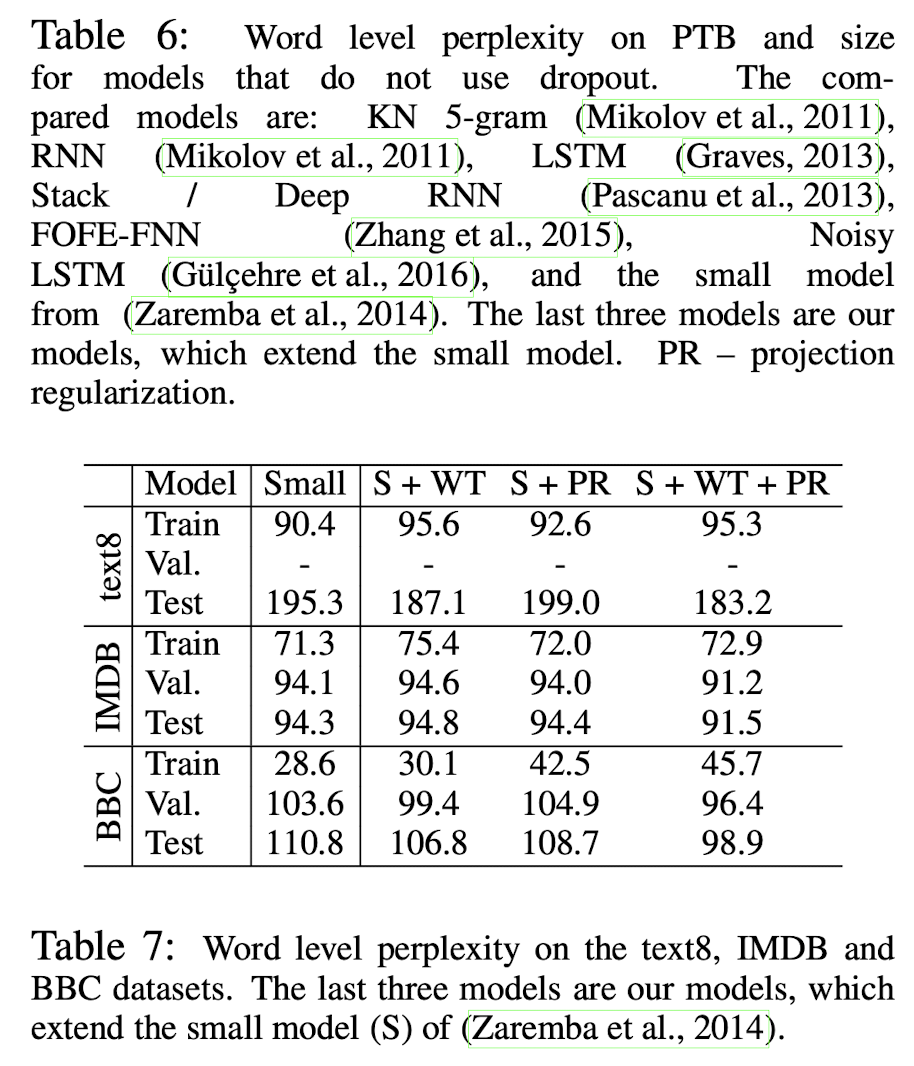
다른 dataset에 대한 결과도 Weight tying(WT)과 Projection Regularization(PR)의 효과를 확인할 수 있다.
Neural Machine Translation
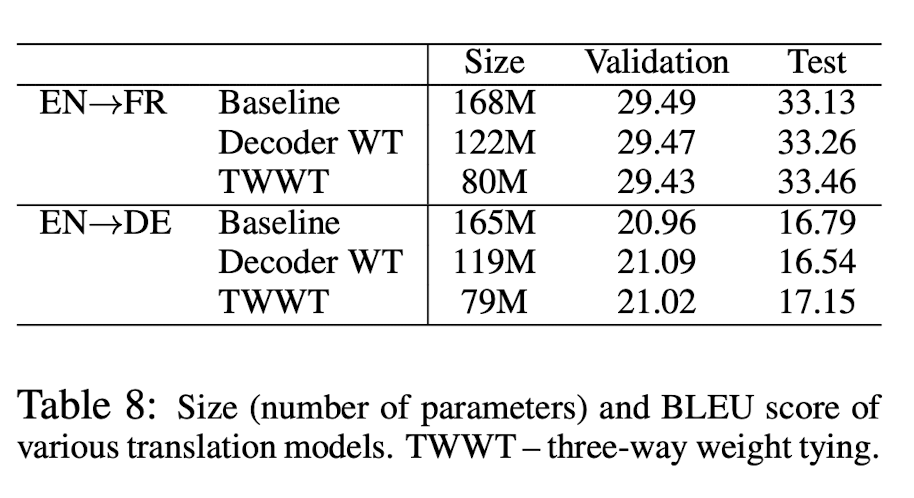
마지막으로, Neural machine translation task에서의 실험 결과이다.
논문에서는 Decoder의 input, output embedding만 tying한 결과와, decoder의 input과 output embedding을 tie하는 것을 넘어, encoder의 input embedding까지 tie하는 Three way weight tying (TWWT) 결과를 같이 제시했다.
성능 자체는 큰 차이가 없지만, model size를 같이 봐야한다. Weight tying(WT) 기법이 적용된 model은 size(parameter 개수)가 눈에 띄게 줄어드는 것을 확인할 수 있다.(decoder WT의 경우 28%, TWWT의 경우 52% 감소하였다.)
Embedding vector의 weight를 같게 하는 weight tying에 대해 연구한 Using the Output Embedding to Improve Language Models 논문에 대해 리뷰해보았다. 각각의 embedding matrix의 weight를 공유하여 성능을 유지한 채 model의 size를 줄일 수 있다는 것이 인상적이었다. 다만, Three way weight tying (TWWT) 부분에서, 한국어-영어와 같이 비슷한 문자를 사용하지 않는 source 와 target에 대한 Three way weight tying (TWWT)에 대해서 조금 더 찾아봐야 할 것 같다.




댓글